Change Language :
iglidur® N54 - Material data
Material table
General specification
Unit
iglidur® N54
Test method
density
g/cm³
1,13
Colour
green colour
max. Moisture absorption at 23°C/50% room humidity.
% by weight
1,6
DIN 53495
max. total moisture absorption
wt.-%
3,6
Sliding friction coefficient, dynamic, against steel
μ
0,15-0,23
pv value, max. (dry)
MPa x m/s
0,5
Mechanical specification
flexural modulus
MPa
1.800
DIN 53457
flexural strength at 20°C
MPa
70
DIN 53452
Compressive strength
MPa
30
maximum recommended surface pressure (20°C)
MPa
36
Shore D hardness
74
DIN 53505
Physical and thermal specification
Upper long-term application temperature
°C
+80
Upper short-term application temperature
°C
+120
Upper short-term ambient temperature1)
°C
+140
Lower application temperature
°C
-40
thermal conductivity
W/m x K
0,24
ASTM C 177
coefficient of thermal expansion (at 23°C)
K-1 x 10-5
9
DIN 53752
Electrical specification
Volume resistivity
Ωcm
< 1013
DIN IEC 93
surface resistance
Ω
< 1011
DIN 53482
- Without additional load; no sliding movement; relaxation not excluded
Table 01: Material data
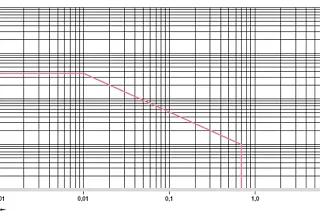
diagram. 01: Permissible pv value for iglidur® N54 plain bearings with 1 mm wall thickness in dry operation against a steel shaft, at +20 °C, installed in a steel housing
X = surface speed [m/s]
Y = load [MPa]
iglidur® N54 is the first iglidur®material that is largely based on biopolymers. In addition to the fact that all iglidur®materials are already lubricant-free, this is a further step towards a positive environmental balance. Good coefficients of friction coupled with service lives that allow series use in sporadically moving applications give this material a firm place in the iglidur®programme.
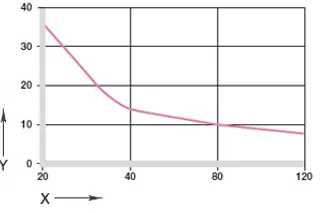
diagram. 02: maximum recommended surface pressure as a function of temperature (36 MPa at +20 °C)
X = temperature [°C]
Y = load [MPa]
Mechanical specification
The maximum recommended surface pressure is a mechanical material parameter. It cannot be used to draw conclusions about the tribology. The compressive strength of iglidur® N54 plain bearings decreases with increasing temperatures. diagram.02 illustrates this relationship. At the long-term permissible application temperature of +120 °C, the permissible surface pressure is still just under 10 MPa.
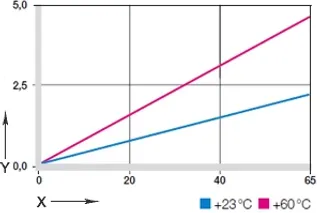
Diagram 03: Deformation under pressure and temperature
X = load [MPa]
Y = Deformation [%]
diagram. 03 shows the elastic deformation of iglidur® N54 under radial load.
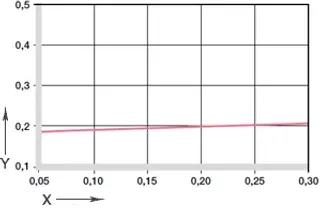
Diagram 04: Coefficient of friction as a function of the surface speed, p = 1MPa
X = surface speed [m/s]
Y = coefficient of friction μ
Friction and wear
The coefficient of friction of iglidur® N54 is low. However, it must be noted that an excessively rough sliding partner increases the friction. We recommend a shaft roughness (Ra) of 0.1 to a maximum of 0.4 μm.
The coefficient of friction of the iglidur® N54 bearing is only slightly dependent on the sliding speed.
The influence of the load is greater, with the increase of which the coefficient of friction drops to 0.8.
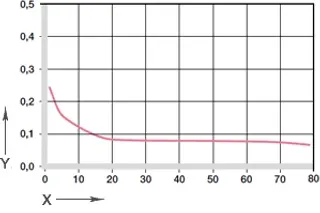
Diagram 05: Coefficient of friction as a function of the pressure, v = 0.01m/s
X = load [MPa]
Y = coefficient of friction μ
iglidur® N54
dry
Grease
oil
water
coefficient of friction µ
0,15 - 0,23
0,09
0,04
0,04
Table 04: coefficient of friction for iglidur® N54 against steel
(Ra = 1 µm, 50 HRC)
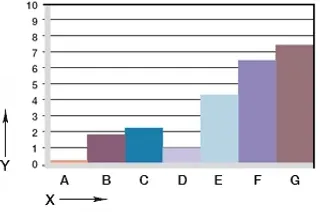
diagram. 06: Wear, rotating application with different shaft materials, p = 1 MPa, v = 0.3 m/s
X = Shaft material
Y = wear [μm/km]
A = aluminium, hard anodised
B = free cutting steel
C = Cf53
D = Cf53, hard chrome-plated
E = HR carbon steel
F = 304 SS
G = high grade steel
Shaft materials
It is important to select the suitable shaft material. it cannot be said in general that iglidur®® N54 is better suited for hard or soft shafts, but "hard" shaft surfaces tend to lead to better service lives. At loads from 1 MPa, the wear increases noticeably and continuously.
Contact us
Contact details

Opening hours
Office hours
Monday to Friday from 8 am - 8 pm.
Live chat:
24h

